Your guide to educational app services
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
Why EdTech?
Today, education has to be collaborative and interactive. Gone are the days when students sit in the classroom and learn solely by listening to lecturers. Fortunately, the tables are starting to turn. Technology is opening up a world of endless possibilities for extending the classroom beyond its four walls. And people are starting to make the most out of it.
EdTech is the short word for Education Technology and it refers to the new technologies implemented in the field of education, both in classrooms and at home. The EdTech current started in the 90’s and kept growing ever since. The 2020 Covid Pandemic boosted up the transition to technology in the education field due to the massive disruptions caused by the lockdown measures. The world wide market size for EDTech was $163bn in 2019 and is expected to grow to $416bn in 2025. This represents a 2.5x increase that will bring significant opportunities for entrepreneurs.
Every single child has the right to education, as stipulated in the Convention of the Rights of the Child. Education is closely associated with higher-paying jobs, a healthier life, social security, and opportunities for full participation in society. However, until this day, there are children whose right to education is still denied.
Education is what sits at the basis of human progress. For many years now technology has started to support different education parts and the Covid pandemic has accelerated this progress. Still, there are a lot of challenges that the education systems are dealing with that can be transformed into growth opportunities.
Based on the challenges detailed below, the opportunities that EdTech sees for the next period revolve around increasing the technology reach and affordability, the quality of education, the sustainability and the security of the products. Additionally, ethics, diversity and inclusion will also be major areas to take into consideration in the next few years.
Challenges and growth opportunities in the EdTech industry
Logistics – children still have lots of physical materials that need to be procured and carried around
In most cases, the teaching methods are not interactive, or as interactive as they could be
Equitability – reducing the difference in terms of opportunities for children coming from different areas or environments. It is very hard to say today that a kid in London has similar opportunities as a kid in Congo. There is a digital divide between those who have the technology at home to continue their education outside the classroom and those who don’t. That’s the first thing that should be addressed - accessibility. We have to make sure that everyone has access to hardware and software and of course, to a reliable internet connection.
Accessibility - one of the most marginalized and excluded (willingly, or not) groups in society: children with disabilities should have access to education in the same way that the other kids do.
Adaptability – people have different needs when learning and the education process is not adapted per individual.
Access to technology (internet, laptops, tablets) is another challenge that many education systems are facing.
Children's security – technology may be Pandora's box and can bring multiple challenges that need to be addressed.
High school dropouts - Every year, over 1.2 million students drop out of high school in the United States alone.
Teachers training - teachers aren’t very well trained in how to use digital tools in a way that can help students and improve educational outcomes. There’s a gap there because they are trained in how to teach face-to-face, and how to get through lesson plans. However, there are now so many other tools that can be used to elevate teaching methods, but the lack of training means that their use in those lesson plans gets ‘muddled.’
Curricula is outdated most of the time - there is a need for curriculum design to consider the different demographics of every class and school. Schools craft curriculums for the entire year, and they don’t really ever break from that. But there are certain trends and changes that might take place throughout that year, and yet curriculum design is not able to keep up, it needs to be adjusted. Technology and software can pinpoint and predict trends and changes, and can help with that.
Unfortunately, the education sector still has a lot of catching up to do. A recent UNICEF report revealed that more than 200 million school children live in countries that are still unprepared to implement remote learning in case of emergency school closures. Due to this lack of preparation, nearly half of these schools stayed closed for at least half of the Covid19 pandemic.
However, one thing is clear: there is no going back to the way things were before. Consequently, adapting to this new, digital-focused environment is crucial for any type of business, including those related to education.
Why digitalization is essential for the Education industry
Before we dive deeper into the benefits and challenges of digitalization in the education sector, let’s go over what this concept means. Often used interchangeably, digitization and digitalization need to be clearly distinguished in the context of digital education.
What is the difference between digitization and digitalization
Digitization relates to the process of converting physical aspects of education into digital formats (e.g. developing courses in an electronic format, taking notes in an app instead of a whiteboard or piece of paper, teaching classes via Zoom instead of in the classroom, and so on);
Digitalization refers to the conversion of current education and training processes with the help of digital technologies. The key purpose of digitalization is not to just ‘go digital,’ but to add value and increase effectiveness through modern technology, so it’s the next step over digitization.
Benefits of education digitalization
Over the past two years, we’ve worked with various clients in the education sector, helping them digitize and digitalize their products and services. During this time, we’ve discovered firsthand the many benefits of going digital in this industry, and here are just a few of them:
Information sharing and accessibility
The most important benefit of digital education is undoubtedly accessibility. Anyone can further their education and learn new skills with just a few clicks on a device of their choice. Digitizing educational materials unlocks opportunities for people all over the world, and makes it easier for students to access materials, without having to buy, borrow, or xerocopy books.
24-hour availability
How many people living outside the U.S. can dream of attending classes at Harvard or Stanford? With online education, that dream can come true. Most major universities around the world offer online courses and training programs that you can attend from the comfort of your home. An added benefit is asynchronous learning, which allows you to study when you are most comfortable and productive, whether that’s late at night or the crack of dawn.
That’s just one of the benefits of 24/7 availability; there is evidence that online learning can be more effective than in-person learning, in several ways. Data from The Research Institute of Americas shows that, on average, students retain 25% to 60% more information when studying online, compared to just 8-10% in a classroom. Why? Because students can learn at their own pace, going back and re-reading, or going through the material as they choose.
Cultural diversity
We are living in a globalized world, and it’s becoming clear that to operate and be successful in any field, you need to understand cultural differences. But in traditional education systems, we don’t often get a chance to interact with colleagues from all over the world. With online learning, you can connect to and interact with people from all over the world, people who have different backgrounds and ideas, and learn from each other. That, in itself, is a unique way of expanding your education and being more open-minded and knowledgeable about other cultures.
A global market for teachers
Online learning doesn’t only bring benefits for students - it also helps teachers. There is no physical limit to how many students you can teach online, while you have limited space in a classroom. Teachers and tutors also have easy access to tools and courses to further their education, earn CE credits, learn new skills, and advance in their careers. This, in turn, will make them better at teaching and help them embrace new teaching methods.
Digitalization perks
By using modern technology, it becomes much easier for schools to perform administrative tasks. There was a time when teachers and superintendents would spend countless hours doing reports and paperwork. With the help of digitalization, these tasks can be simplified, integrated, and even automated, saving schools and teachers a lot of time and effort.
Another perk of digitalization is the opportunity for gamification. This is a proven strategy to motivate students and pique their curiosity; gamification also ensures students remain engaged and interested in what teachers have to say.
Last but not least, digitalization can improve your bottom line. Overall cost reduction is real, and sometimes it can be significant because online learning means reducing commuting costs and school utility bills. It also means going paperless, which is not only more cost-effective but also environmentally friendly.
Feedback loops and adaptation
With digitalization, making informed decisions becomes so much easier. You can identify and track performance KPIs very easily when learning online, because you have all the necessary data at your disposal, just a few clicks away. Digitalization also helps you adapt and implement feedback at a much quicker rate than in the conventional education system.
Type of education apps to develop
Education Technology applications aim to promote, simplify, and enrich the teaching process by integrating technology into the learning environment.
Ideally, the educational process does not have an end, being a lifelong activity.
Depending on the user type, there are multiple types of educational apps. As such, we can differentiate the following types of educational apps:
Kid-focused educational applications
All educational apps should ideally revolve around the children themselves at the end of the day, but this particular category is special, as it puts the kids straight in the driving seat.
Whether it’s a simple digital toy-book with a child-friendly UI, or a multi-level video game with sophisticated animations, kid-focused learning apps are by far the most challenging to build. To develop for a child you need to think like a child, which is a skill that’s easy to forget and extremely difficult to relearn.
Education apps aimed at teachers and students
No amount of code will ever replace a great teacher, but a clever app can take their work to the next level. From single-user apps for classroom management, adding a twist to a presentation, grading or tracking attendance, to multi-user platforms for quiz games, submitting questions, or class polls, there’s a wide array of teacher-aids on the market.
Reference apps – for storing and managing learning material
Why waste resources printing and shipping heavy textbooks when you can have all the content within an app? Not to mention the hurdle of carrying them around all day, or the precious minutes wasted looking for the highlighter (arguably the most frequently misplaced object in any student’s arsenal). Once the materials are in a cloud, assigning homework is also as easy as sending a link.
Employees education apps
Employee education is crucial as It ensures a competitive edge in the market and it reduces technical mishaps, promotes safety and health among employees. Training your team directly correlates with better productivity. Training enhances the efficiency of employees and hence productivity and profitability.
Additionally, It creates opportunities for career development and personal growth of employees. Training equips employees with better knowledge which helps them in their career trajectory.
To keep up with the competitive environment, training for the employees is the most viable solution. Companies incur considerable expenditures to assist employees through employee training. Companies like Amazon and Pixar spend a massive amount of money in offering excellent training and development programs.
However, it becomes difficult for companies to organize continuous in-person training with a large employee base. Here comes the role of E-learning in employee Training.
E-learning is the method of engaging in an educational course in an online setting. E-learning courses can use various techniques, for example, audio and video recordings, presentations, quizzes, surveys, games, discussion groups, and more.
The prime advantage of E-learning methodologies over conventional training methods is that it saves a considerable amount of time and money. Also, it eliminates the constraints of distance. You can train your employees in remote locations in a consistent and structured manner.
Also, companies can easily incorporate Elearning programs into the busy schedule of employees. It is beneficial to both employees and employers. Its easy accessibility and broader reach present added advantage.
Administrators aid applications
Teachers and students are taking more and more advantage of technology in their day to day activities. However, when discussing edtech we should not forget to consider also the people behind the doors. There are a lot of activities that need to be done so that a school or a university can function. Therefore there are also education technology products that are aiming to help the administration staff of each institution.
In this section we are referring to CRM systems that help universities follow their leads, SIS systems that store information relating to students all along their study journey or any other type of product that helps institution admins to become more efficient, productive or increase data security.
Why you should have a mobile first approach
What is the first thing you reach out for when you wake up in the morning?
We’re going to take a wild guess and assume it’s your smartphone. Even if it’s just to turn off your alarm or look at the time, it’s more than likely that your phone will be the first thing you touch in the morning.
We’ve become so attached to our smartphones (some would even say dependent or addicted, but we won’t go there) that it’s impossible to imagine our lives without them. Just think about it; what if apps like Facebook, Instagram, Google Maps, Spotify, or Revolut didn’t exist? What if you could only access these platforms on a desktop computer? If the mere thought sends shivers down your spine, don’t worry, you are not alone.
Roughly 6.4 billion people own a smartphone in 2021, and that number is on the rise. Statista predicts that 7.5 billion people will own a smartphone by 2026. Given that there are currently about 7.9 billion people on the planet, it’s fair to say that smartphones are here to stay - and so are mobile apps.
In this digital, tech-savvy, device-focused era we’re living in, failing to embrace or even consider a mobile-first strategy can significantly hurt your business. As of October 2021, mobile usage rests at 54.37% of the global market share, with desktop usage at 43.15%. What’s more, experts predict that mobile e-commerce sales will reach $3.56 trillion by the end of the year. Not focusing your efforts on reaching mobile users is, therefore, more than a missed opportunity. It can hurt your bottom line and the overall success of your business.
Having worked in the mobile app development world for a while now, we’ve seen firsthand how much of a difference a mobile-first strategy can make. That’s why we want to dive into this topic and explain why a mobile-first approach is a good idea for your product and your business. We hope that by the end of these paragraphs, you’ll have a greater understanding of why this strategy works, what it entails, and whether it’s the right direction for your business goals.
First thing’s first: let’s define and understand what ‘mobile first’ really means.
The concept was popularized by Luke Wroblewski in his 2009 book, titled - you’ve guessed it - ‘Mobile First.’ A mobile-first strategy is a business development approach that prioritizes mobile users over desktop users. This type of approach is not limited only to the UI/UX design or the technology platform. Instead, it covers the entire product-building mindset.
Of course, a mobile-first strategy doesn’t mean you shouldn’t also provide your users with a great web experience. But a mobile app will enable you to provide a more well-rounded, complete customer experience that will keep users returning to your product.
Making your mobile users your top priority can bring numerous benefits and help your product achieve long-term success.
Here are some of the most important benefits of a mobile-first strategy:
A wider reach
If you only allow your users access to your product from a computer or laptop, you will miss the opportunity of reaching millions of mobile users out there. As smartphone and tablet screens get bigger, students are spending more time on these devices and less time on their computers. What’s more, for mobile users, responsive web design won’t cut it. To get their attention and loyalty, you’ll need a dedicated mobile app that’s always present on their screens, ready to be accessed.
Mobility
If your product or service is only accessible via a desktop computer, you’ll significantly restrict your potential user pool. Not to mention you will rely on access to an internet connection at all times. Students nowadays are constantly on the move, and they’re no longer tied to their laptops or computers for work or leisure. Having a mobile app allows the student to access and take your product anywhere, anytime. Whether they’re at the coffee shop or the grocery store, on the bus, or even in the bathroom, they will be just a screen tap away from your product or service.
Customization
With a dedicated mobile app, you unlock access to various customization options to attract and retain customers. Mobile users have come to expect a flawless app experience, so you will need to invest time and effort in your UI/UX design and make sure that everything works smoothly. However, if you do get it right and provide users with a seamless mobile experience, it will be worth it. Users will return to an app that is easy to use, has an intuitive UI, and works flawlessly every time. Keep updating, upgrading, adding new features, and improving on your app, and your efforts will pay off.
A superior customer experience
For most products, a seamless mobile experience coupled with an intuitive, clean, and fast-loading website will work best to attract and retain customers. This way, you’ll make sure you reach both mobile and desktop users. What’s more, by allowing them to access and interact with your product in different ways, you will be able to provide a superior and complete customer experience. Your mobile app will allow you to narrow your focus and showcase the best features of your product, while your website will offer users the opportunity to explore your offerings on a deeper level.
An edge on the competition
Given the stats we discussed at the beginning of this article, it wouldn’t be a stretch to say that we might be heading towards a mobile-first existence. What if desktop computers and laptops were to become obsolete or only used for certain tasks? Wouldn’t you like to know about it beforehand and be ahead of the trends? A mobile-first strategy will allow you to do just that. It will be much easier to adapt to new technologies and trends with a fully functional mobile product and an established mobile user base. Think of what happened during the Covid19 pandemic, as lockdowns and restrictions forced many businesses to move online. Those who already had a strong online presence were at a clear advantage, and that’s precisely what you want - to be prepared.
The blueprint of any education app
Important functionalities to keep in mind when talking about an educational app
In terms of the most general features, children’s apps aren’t all that different from the rest, however there are a few additional boxes that an educational app might need to check.
Important aspects to keep in mind when developing an app for children
Kids’ brains work differently, so an app built specifically for them must follow different usability guidelines and design language. With that said, you don’t have to throw out the UI/UX textbook just yet. In fact, the impact of UI decisions such as simplification often has a multiplier effect on usability when you’re developing for kids.
Build for exploratory behavior
When building an intuitive UI for adults, the starting point is to try and recreate familiar patterns. This is driven by a simple goal, the very reason why they downloaded your app in the first place: get the job done as quickly and efficiently as possible. They like to stick to the beaten path, and if the interface stands their way, they’ll be quick to look for another app that won’t.
Children’s brains are hardwired to learn new things, and they don’t have preconceived notions about how an app should work. They’ll mine-sweep the screen, pressing every single button until they understand what each one does. However, their curiosity and craving for entertainment doesn’t guarantee they’ll always find their way around a convoluted interface. On the contrary – the layout of a kids’ app must be logical and simple, especially if you’re targeting younger children. They tend not to use the ‘Back’ button for example, which is second nature to adults and also expected by older kids. They also want instant gratification, so they’ll give up in the blink of an eye if something doesn’t work.
Colors are everything
Colors are really important, but ‘colors are everything’ is not the same as saying everything needs to be colorful or that you should use all the colors of the rainbow. Children are intuitively drawn to vivid colors, as well as animated movements and interesting sounds. But it’s just as easy to overwhelm them as it is to catch their attention.
Sensory attraction shouldn’t mean disorder. If too many elements are simultaneously competing for children’s attention, they get confused. They won't know what to focus on. Aim to find a good balance of movement, sound, and color, and although it’s a different scale from apps designed for adults, the ‘less is more’ philosophy is still a safe approach. Keep the ultimate goal in mind when choosing colors and animating: helping kids achieve their goals, keeping their attention focused on the task.
Accessibility compliance is a must
It’s important to know that digital accessibility in educational places is mandated by US case law and federal regulations. The phrase 'accessibility' refers to four different aspects – vision, auditory, motor, and learning & cognitive – and the WCAG 2 (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) international standard, (WCAG) describes detailed methods on how to make web material more accessible to people living with disabilities.
However, EdTech accessibility goes beyond legal standards and augmenting interfaces. To improve students' overall learning experience, you should prioritize digital accessibility from the get-go. And not just for children with disabilities. Everyone benefits from accessible design since it focuses on creating a comprehensive experience, removing obstacles, and allowing everyone to benefit from your educational app.
There’s no such thing as ‘designing for kids’ – Age-appropriate design is key
They grow up so fast – the phrase might have been coined by grandparents, but it’s being adopted by app makers. As children’s behavior and skills develop with lightning-speed, you almost cannot go too narrow with age groups when designing for children. You should at the very least think in three-year age intervals to have a chance at nailing the design, but as a rule of thumb, the younger the audience the narrower you should pull your focus.
Differences in children’s in-app behavior compared to adults
How to build an end-to-end education app
One of the key details for building a successful application is to understand and follow the entire product development journey. Although building the application takes most of the attention for most of the entrepreneurs, there are certain steps that need to be taken to increase the chances of success.
Unfortunately, the statistics you’ve been reading about are true. It’s hard to find a precise number, but it’s fair to say that over 80% of new mobile products end up in failure. What’s more, 80-90% of mobile apps launched on an app store are abandoned after a single use. This can be devastating for someone who has dedicated time, money, and effort toward building a mobile app. That’s why it’s important to plan ahead and work with a product partner to develop an app that people will actually use.
When building a mobile app you should ask yourself the following questions:
Product-market fit - Is the problem you’re trying to solve a real problem? Does it really
need solving?
User persona - Who is your target audience? What are their day-to-day habits, hobbies,
and preferences?
Competitor research - Who are your competitors? What are they doing? What are they not
doing? How can you do it better?
Complexity and usability - How many features will your app include? How will you ensure the
app is intuitive and easy to use?
Business model - How will you monetize your product? Will you offer a free trial or a
freemium/premium subscription?
Marketing strategy - How will you market and advertise your product? Which marketing
tools make sense for your product? (social media, PR, advertising, etc)
Operating systems - Where will you launch your app, on iOS or Android? Will you go for
native or cross-platform app development?
Testing & QA - How will you test your app before launch? (MVP, proof-of-concept,
prototype)
Analytics - How will you track progress and measure results?
The following steps are also very helpful for setting a solid base when building a new educational product:
Clarifying the promise you are making
The first and most important step of the process is to clarify the promise you are making with your mobile product. What is the problem you are trying to solve, and how are you going to solveit? How is that problem being handled right now, without an app? Is it being handled at all?
When you go to a movie, for instance, you don’t know whether it’s good or bad before you watch it. Still, you choose to see it based on the promise the producer, director, and actors make to you. We make a lot of decisions based on promises and expectations. So, in this first step of the process, we sit together and figure out what promise you want to make to your audience. What is it that you are trying to solve? How will your product improve their lives? Is your promise too big, or too small? These are the questions we’ll be asking during this phase.
Identifying your target audience
One of the most vital steps in the product development process is identifying your target audience. We help you do this by asking as many questions as possible about your ideal target audience to learn more about who your product caters to.
In this stage, we try to create a profile of the people who are most likely to use your product.
Who are you targeting with your mobile product? How old are they? What are their interests and hobbies? What’s their location and education level? What’s their job role and what industry do they work in? What kind of platforms and devices are they using? What types of apps are they already using? How do they interact with the world around them? What are the problems they’re facing and how can your app help improve their lives? These are some of the questions you should be asking yourself before developing your mobile app. Then you can start focusing your efforts on making sure your product is what your users need.
Positioning yourself in the market
The next step in the pre-launch phase of the product development process is positioning. During this step, we work together to figure out if you’re the Volvo or the Lamborghini of the edtech market, so to speak. It’s important to understand where your product will sit in the market. Competition is intense, and with so many mobile apps being launched daily, it’s hard to stand out. That’s why you want to establish a clear, unique identity and allow your potential customers to identify you easily.
This is the time to run a thorough competitor analysis, to see who you’re competing against in your market. Look at what your competitors are doing, and how they’re doing it. What would you improve on, and what can you bring to the table? What’s more, look at what they’re not doing; if your product offers a valuable feature that none of your competitors have, it’s good to focus on that. Then look at the actual design and usability of other similar apps. What do they look like, and how easy are they to use? It’s important to look for ways to differentiate yourself from otherplayers on the market, and we’ll help you do just that.
(In)validating your product
Once we’ve figured out who you are, what you’re planning to offer, and to whom, we can start
discussing what we are going to build. This is not as easy as it sounds. We will need to think
broadly about the product requirements and gradually narrow them down to what brings the most value to your customers.
One of the most important things we’ve learned thus far is that, if your product is going to fail, it should fail fast, to limit the losses. So, at this stage of the process, we analyze and determine what is the minimum viable product (MVP) we need to build. Depending on the type of app you want to create, we’ll create either an MVP, a prototype, or a proof-of-concept for your app. A proof-of-concept is usually needed when you want to test the technical feasibility of a product,
while a prototype relies heavily on design and is basically a trial version of your end product.
Designing your mobile product
After going over your product idea and figuring out what features it should include, it’s time to start working on the app itself. We begin this next phase of the process by focusing on UI and UX. The user experience is arguably the most important aspect of your mobile app, as it defines how people interact with the product and what that interaction feels like for them. You want your app to look good, but also to be intuitive and easy to use. Keep in mind that mobile users tend to interact with mobile apps on the go, and they don’t want to waste time figuring out how an app works. What’s more, if a user is not happy with an app on the first try, chances are they won’t be using it again, and that’s something you really want to avoid.
Development & QA
Here comes the fun part...at least as far as we’re concerned. The development stage of the
product is where all the ideas we’ve been discussing finally come to life. This is where our team thrives, and we go all in to create a fast, intuitive, and fully functional mobile product for our client. The way we work is by using an agile approach to the development process. Consequently, we split the scope into two-week sprints, and deliver incrementally towards the MVP launch.
We are always fully transparent towards the client during the development process, so that you feel involved and part of the team. We’ll have a clear communication plan in place and host a demo session every two weeks to check our progress and get the client’s input. Our team will make tweaks and adjustments where needed, to ensure the usability and functionality of the app. As far as the budget goes, we work together to make sure we have the most efficient approach to sustain the next stages of the process without overspending.
Launching your product
After the development stage comes the most exciting step of the entire process. Some would say it's also the most anxiety-ridden step, which is understandable. This is the moment we’ve all been waiting for: launching your mobile product into the world. We’ll help you with all the pre-launch details, like submitting your app to the app store, and crafting your story for your investors, customers, and competition.
This is also where marketing will start playing a big, big role. Depending on the type of app you’re launching and your overall marketing strategy, you might launch a press release announcing the app, send out an email blast, run a social media campaign, invest in advertising, and so on.
Collecting feedback & data
You must have analytics and monitoring tools in place before officially launching your app. The early days of a new mobile product are crucial, so you’ll want to make sure that everything works smoothly and that users are not encountering any issues with downloading, installing, or using your app. It’s essential to track everything at this stage, to see who is using your app, how they’re using it, and compare this data to your initial plan.
Product increment & scaling
Let’s say you’ve launched your new mobile product, and it’s doing very well in the market, even exceeding your expectations. Sure, it’s time to celebrate, but don’t rest on your laurels just yet. This is a crucial moment in the product lifecycle, where we plan to scale your product and ensure it continues to improve and grow.
What risk factors should be taken into account
Regulatory
Just as many other industries like Health, Transport, Gambling, the EdTech industry is getting to be more and more regulated. The sudden burst in edtech activity coupled with the lack of an adequate regulatory framework allowed some questionable practices along the way. Governments and NGOs are trying to tackle this issue and should be supported.
Private organizations started to certify the quality of EdTech products. One example is the Education Alliance Finland.
They provide a product evaluation & certification service based on global quality standards for learning solutions. Their service helps to improve product's pedagogy and offers an agile way to demonstrate educational impact to your customers.
Technology accessibility
Although the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the technologization of the education field, there is still a large gap between the western society institutions and the rest of the world. Therefore currently there is a risk that even if you build a brilliant product the students that are able to use it are limited.
Security
Taking into account how vulnerable the users targeted in the EdTech segment is, one of the major concerns for the users and organisations is the security of the product. Unfortunately there have been numerous security breaches in edTech products during the last years. One example is the Chegg incident.
Slow monetization
Although we consider education to be one of the main pillars for human progress from a financial perspective, the industry is not as attractive as other industries such as health, entertainment or finance from an investment perspective.
The investors are not forming queues at the edtech companies entrance to throw money at them, however there are plenty of opportunities in accessing government grants and funding.
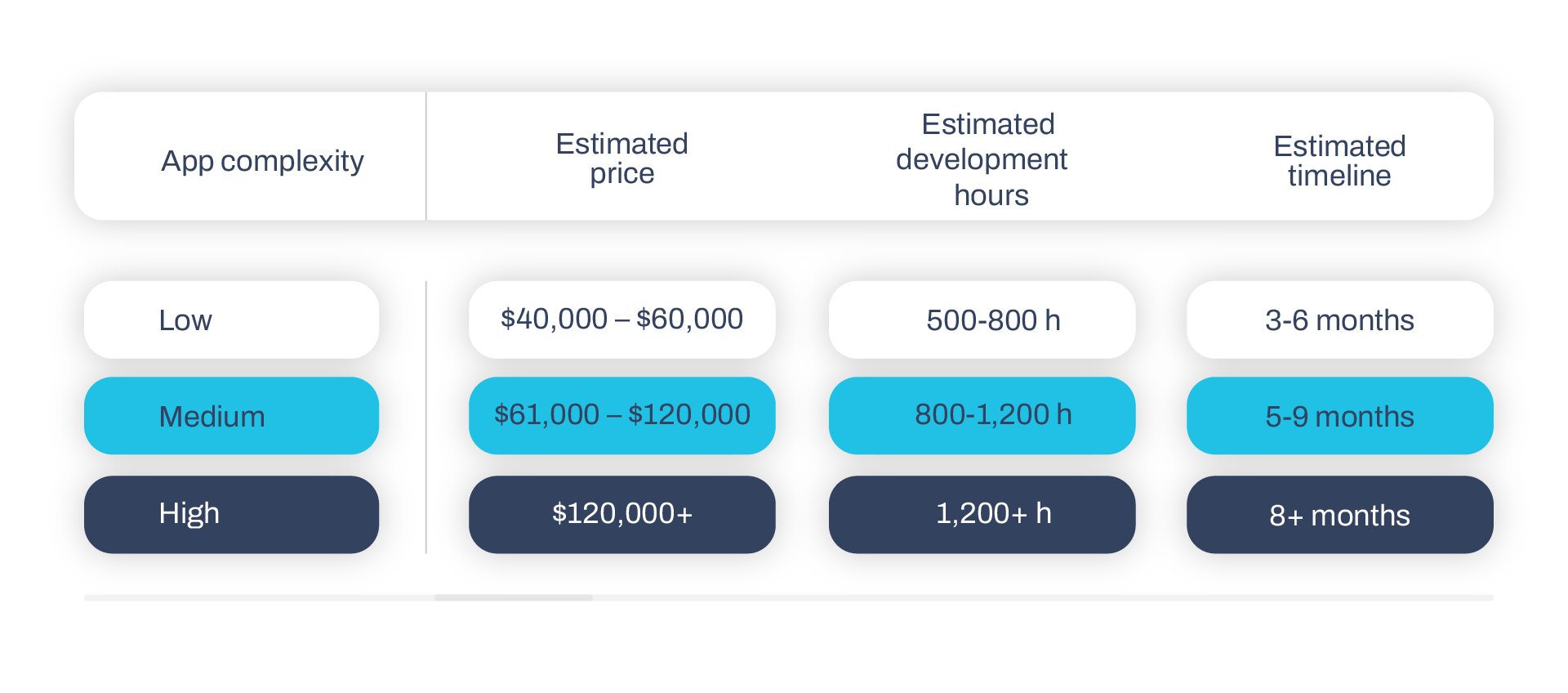
The real cost of an educational app
Estimating the cost of an educational mobile application is not that simple, and it depends a lot on the purpose, audience, and technologies being used. But the complexity of these projects is what motivates us at X2 Mobile, and we enjoy figuring out every detail. We take the time to understand your business’ needs and objectives in order to identify the best options for your goals.
Think about building a house. With the latest tech you can finish a perfectly functional home within a few months out of just $30K and move on to another project. Or you can spend $500K and have a truly exceptional piece of architecture – but it may be a work in progress years after you break ground. Ask yourself what your goal is and how much of your resources you can engage to get there.
However, there are a few app development benchmarks that you can use as a rule of thumb to get a better idea of what the development of your project would set you back. Bear in mind that the range is quite wide, and the price data is aggregated from multiple companies:
The golden triangle rule
1. Time – how quickly you want to build the application
2. Cost – your available budget for developing the app
3. Scope – the functionalities you need to have
These factors are inter dependable. In other words, you can’t modify one of them without affecting the other two.
Baby steps – keep it simple for the first release
Rome wasn’t built in a day, so don’t be afraid to put most of the fluff to the side in the first round. If you postpone as many of the advanced features as you possibly can from the initial release, you not only eliminate a lot of the initial headaches but also save yourself some growing pains from future stages. Don’t worry, you can always add more bells and whistles as you go. Brick by brick.
We always recommend putting a first version of the app in your customers’ hands as soon as possible with just the core functionality.Many small businesses have trouble deciding whether to start with a PoC, create a prototype, release an MVP or dream big and go straight for a full-fledged product. If you’ve paid attention so far you should know that the last option is not recommended, but what about the other three? What are these acronyms anyway?
Proof of Concept (PoC)
In any case the first step is to understand what you’re building. This is where a proof of concept can come in handy, to see whether your app idea is feasible in the first place. A PoC is the fastest and most accurate way to validate or refute your assumptions about users and your concept.
It’s usually a quick internal exercise. PoC focuses on determining whether your concept is possible to develop, and it’s also a good way to share inside knowledge about the product’s basic functionality.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP is the first truly usable form of your complete product – even if it’s a far cry from your final vision and the implementation is not perfect yet.
The idea of an MVP is that when the core functionalities are already in place and there is a value proposition to talk about, your product is ready to dip its toe in the app market.
An MVP allows you to learn how the end users interact with your app, and it’s an important step towards the project fulfilling its business purpose. Of course, the work is far from over at this point, but don’t worry – the goal is to gain as much feedback and usage data as you can, identify user pain points, and put together a to-do list for the future.
Minimum Marketable Product – MMP
It’s getting bigger! While MVPs are mainly used to validate assumptions and start gathering real-life data, the minimum marketable product is expected to not only answer a demand. It should also bring value with an edge on the competition.
The trick is to look ahead and use the feedback gathered in the MVP phase to actually improve the concept, rather than getting bogged down with what needs fixing from the first release. Take the feature requests and enhancement suggestions and analyze them critically to see how you can add the most value to your product. Prioritize the action items by what appeals most to your target demographic.
Your Minimum Marketable Product (MMP) is a stable version of your product or service that withstands the mostly harsher critique of the broad market that you are going to release your product or service to in this phase.
In-house development vs. outsourcing – which is best?
In-house app development
Hiring developers and nurturing a team – making sure they have everything they need to do a great job and deliver on time – is a lot of admin work. Especially if you only have a small project or two, the management costs can far exceed the profit margins of an agency and the investment may fail to reach the ROI you’d get with outsourcing.
We only recommend doing in-house app development if you already have a development team available, sufficient knowledge in the area, as well as a roadmap with several long-term projects.
Outsourcing to a development agencyAlthough outsourcing may sound like giving up control at first, you should keep in mind that third-party developers are like any other business – they can only stay in the game as long as their clients are satisfied. You’re still calling all the shots, and there are some additional advantages to working with a team that builds mobile products daily:
Experience - They’ve already had many of the same challenges your in-house team would be facing, and they’ll come up with solutions much quicker.Resources - You don’t have to bother with holidays, replacements, or performance management. Your project is always the main topic of discussion.
Planning - Keeping the team busy between projects is never a concern. It’s like having developers on a subscription that you can cancel and reactivate as you need.
Contract types and development styles – Waterfall vs. Agile ; Fixed Price vs. TnM
Fixed-price (FP)
With this type of contract you pay a lump sum in exchange for specific results. The fixed price guarantees no budget overruns, so it’s a good alternative if your company has a strict plan for budget and expenses.
However, the low-risk promise of a fixed-price contract may be misleading in some cases.
Since the scope of the application is agreed at the beginning, it often pushes the team to take a waterfall approach, which can translate into more paperwork and less efficiency. Any changes will be charged extra, which might lead to higher costs and extended timelines at the end of the
day.
If you looked at the estimates above and you’re about to wrap up your research, don’t call it a day just yet. It’s important in the beginning to have a rough estimate of what your app would cost you, but at the end of the day, it’s just that: an approximate figure that may lead you down the wrong path.
These ballpark figures can turn out to be a hit-and-miss when budgeting for mobile app development. At the very least, you should take into account some of the next factors as well:
Time and Material (TnM)
Here, instead of paying upfront for an agreed result, you pay the development team by the hour, and for the resources they use for any given phase or project. This type of contract is a clever choice for when it’s difficult to estimate the project’s costs and timeframe, as there’s no set price or rigid deadlines to influence.
TnM contracts go hand-in-hand with the agile approach that involves the development team working together with you to agree on what functionalities bring the most customer benefit and at what time.
5. Technical solution – cross platform vs. native development
6. Estimation and offer
During the initial discussions with a development agency, your focus should be on collaborating and clarifying as many of the unknowns as possible. There are many moving parts to any app development lifecycle, so it’s normal for surprises to appear along the way, but it’s best to try and sort out as much as possible in the beginning.
When budgeting for an app development project, you should consider the following four work stages:
Designs - creating the UX and UI content; .
Development - iOS, Android, Web, and backend; .
Technical solution - native, hybrid, or cross-platform; .
QA / testing - making sure everything works as expected;
Find out how much your app might cost
The cost of a mobile app depends on its purpose, the target audience, the timelines and the technologies being used.
Think about building a house. With the latest technologies you can finish a perfectly functional home within a few weeks out of just $30K and move on to another project. Or you can spend $500K and have a truly exceptional piece of architecture – but it may be a work in progress years after you break ground.
We are here to help you, we just need a couple of details about your project.
Please fill out this cost estimation form and we will contact you shortly.
Case studies
Card Deck
Digital decks for foundational skills instruction
About the app
The Collaborative Classroom Card Deck App is a tool for teachers that provides digital card decks for foundational skills instruction. It encompasses both SIPPS and Being a Reader programs, which support readers in grades K–12 build skills and confidence for fluent, independent reading.
Challenges
Our goal was to successfully replace the physical cards used in classrooms throughout the United States with an iPad application. In the image below, you can see what a teacher had to face every day, these being the cards belonging to just one of the programs we have integrated into the application. Before X2 Mobile came along, many teachers were using rubber bands to keep several bundles of cards in place. As many as 20 cards are reviewed every lesson for a single group of students.
In terms of UI/UX, we had a free hand from the client, their only request being to use the same fonts from the physical cards and Collaborative Classroom’s brand guide. As a nice-to-have, we were asked to make teaching more accessible for children with learning disorders, such as dyslexia.
Solution
After several sessions of extensive research spent on Collaborative Classroom’s Learning Portal watching recorded lessons and reading Teacher’s Manuals, as well as fruitful dialogues with the teachers whose lives we were committed to enhancing, we came up with a preliminary version of the application.
Our visit to Hawthorne Elementary School in Sioux Falls, SD to witness a prototype of the app being used in an actual classroom resulted in a new, more polished and playful design and refined gestures for teachers to mark the sounds or words pronounced by students as either correct (swiping up on a card) or incorrect (swiping down on a card).
To assist children with reading disabilities, the Card Deck App offers an alternative font. Letters’ heavy weighted bottoms indicate direction, and their unique shapes help readers not to confuse similar letters, like “b” and “d” or “p” and “q,” thus increasing readability for students with dyslexia.
Subsequent to launching the iPad application, the client also requested an Android version due to teachers’ high demand. We’re currently working on the design for the mobile version of Card Deck App while keeping in close touch with teachers, constantly improving the application to meet their needs.
“Thank you so much for the creation of the Card Deck App. Teachers are loving it and it has been a huge blessing and a time saver this year.”
— Abby D., Sioux Falls teacher
ClassLink Launchpad
Personalised cloud desktop for schools
About the app
LaunchPad for ClassLink is an iOS and Android mobile app intended for teachers and students to better collaborate in class and outside of school. You have access to all your apps, files and classes from anywhere. Accessible from any device, Launchpad is ideal for BYOD and 1 to 1 initiatives.
To provide the best user experience, we integrated Single Sign-On (SSO) in our app. The users are able to sign in once on a website and afterwards they will be automatically logged in by our app.
Furthermore, using the Remote Desktop Protocol technology (RDP), we provided users the possibility of running existing Windows apps, right from Launchpad.
Within the My Files section are integrated cloud drive services like Google Drive, Dropbox and OneDrive, such that you can access all your files from all your cloud drive services in one screen. Here you are able to upload, delete, and copy files from any service you have enabled. Furthermore, you are allowed to copy a file from one cloud drive service into any of the enabled cloud services.
See our EdTech recommendations
EdTech Garage community: https://www.edtechgarage.org/
EdTech MindCET community Israel: https://mindcet.org/en/
Meet us @EdTech London in 2023: https://londonedtechweek.com